Calling EES from EXCEL
The Professional license provides macro commands that simplify transferring data to or from EXCEL to EES.
Starting with version 12.131, it is possible to call EES from EXCEL. The interaction is made using the SendMessage command. It is possible to transfer data to EES using one or more text files that are used to solve a problem and/or run a series of macro commands. EES then writes output files that are read by EXCEL and displayed in an EXCEL sheet. Both numerical values and plots can be transferred from EES to EXCEL.
An example illustrating the interaction is provided here. An EES program is shown to calculate the performance of a heat pump. The name of the refrigerant and the outdoor temperature are provided to EES in text files. EES calculates the COP, heating capacity and refrigerant flowrate and returns this information to EXCEL. EES also provides a Pressure_Enthalpy plot for the refrigerant showing the state points of the refrigeration cycle. This plot is displayed in the EXCEL sheet.
The EES program is very similar to the example Heat Pump COP vs Ambient Temperature in the Plotting section of the Examples menu. It is listed here.
"!Heat pump cycle with heat exchange considerations"
$UnitSystem SI C kPa kJ mass deg
$TabStops 3 in
$DefaultDir 'C:\EXCELEXAMPLE'
$Import 'Refrigerant.dat' R$
$Import 'OutdoorTemp.dat' T_amb
"!Evaporator"
Alpha=0.75 [kW/C] "HX effectiveness-capacitance rate product"
Q_evap=m_dot*(h[1]-h[4]) "energy balance"
Q_evap=Alpha*(T_amb-T[1]) "heat transfer relation"
"!Compressor"
x[1]=1 "saturated vapor at compressor inlet"
P[1]=Pressure(R$,T=T[1],x=x[1]) "evaporator pressure"
h[1]=Enthalpy(R$,T=T[1],x=x[1])
s[1]=Entropy(R$,T=T[1],x=x[1])
s_ID[2]=s[1] "ideal compressor is isentropic"
P[2]=Pressure(R$,T=T[3],x=0) "compressor exit pressure"
h_ID[2]=Enthalpy(R$,P=P[2],s=s_ID[2])
W_c_ID=-(h_ID[2]-h[1])*m_dot; "power requirement for ideal compressor"
ComEff=0.60 "Isentropic efficiency"
W_c=W_c_ID/ComEff "power requirement for actual compressor"
h[2]=h[1]-W_c/m_dot "energy balance on adiabatic compressor"
VolFlow=m_dot*Volume(R$,T=T[1],x=x[1])
VolFlow=4.3E-3 [m^3/s] "compressor volumetric flowrate"
"!Condenser"
T_H=20 [°C] "building air temperature"
Beta=1.0 [kW/C] "HX effectiveness-capacitance rate product"
Q_H=Beta*(T[3]-T_H) "heat exchanger relationship"
Q_H=(h[2]-h[3])*m_dot "energy balance"
h[3]=Enthalpy(R$,T=T[3],x=0) "saturated liquid at condenser outlet"
P[3]=Pressure(R$,T=T[3],x=0) "condenser pressure"
"!Valve"
h[4]=h[3] "valve is isenthalpic"
P[4]=P[1]
x[4]=Quality(R$,h=h[4],P=P[4]) "quality at evaporator inlet"
COP=Abs(Q_H/W_c) "Definition of coefficient of performance"
$Export 'HeatPumpResults.dat' COP, Q_H, m_dot
$PropertyPlot R$ PH 2 T_amb T_H DEF DoQLines Name='PH_plot'
$OverlayPlot 'PH_plot' Table=ARR X= h[i] Y=P[i] pointLabels ConnectLasttoFirst AutoUpdate Color=Green LineStyle=3
$ExportPlot 'PH_plot.jpg' 'PH_plot'
When the Solve command is issued (either from EES or EXCEL) EES will import the refrigerant name and outdoor temperature from text files specified using the $Import directives. EES does the calculations and outputs COP, Q_H and m_dot to file C:\EXCELEXAMPLE\HeatPumpResults.dat using the $Export directive. EES also creates a pressure-enthalpy plot for the specified refrigerant and overlays the P-h data for the states in the refrigeration cycle. The plot is then exported to file PH_Plot.jpg using the $ExportPlot directive.
To control this EES program from EXCEL, it is necessary to create a Visual Basic Application (VBA). Start EXCEL and click on DEVELOPER tab. Select Visual Basic from the EXCEL menu. Create a module and enter the folowing VBA program.
Public Const ExampleFolder As String = "C:\ExcelExample" 'Constants and declarations
Public Declare PtrSafe Function SendMessage Lib "user32" Alias "SendMessageA" (ByVal hwnd As
LongPtr, ByVal Msg As Long, ByVal wParam As LongPtr, ByVal lParam As Any) As LongPtr
Public Declare PtrSafe Function FindWindow Lib "user32" Alias "FindWindowA" (ByVal lpClassName
As String, ByVal lpWindowName As String) As LongPtr
Public Const hwnd As LongPtr = 0
Public Const wm_RunEES As Long = 32777
Public Const em_LogOff As LongPtr = 1
Public Const em_LogOn As LongPtr = 2
Public Const em_Solve As LongPtr = 10
Public Const em_SolveTable As LongPtr = 11
Public Const em_RunMacroTab As LongPtr = 20
Public Const notUsed As LongPtr = 0
Public Result As LongPtr
Sub DeleteFile(FileName As String) 'Delete Filename if it exists
On Error Resume Next
Kill FileName
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
Function OutputFileExists(FileName As String) As Boolean 'Return true if Filename exists
OutputFileExists = (Len(Dir(FileName)) > 0)
End Function
Sub DeleteLastAddedPicture() 'Delete the previous plot
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
If ws.Shapes.Count > 0 Then
ws.Shapes(ws.Shapes.Count).Delete
End If
End Sub
Sub InsertJPG(Path As String, TargetRange As Range) 'Copy a .jpg file name into the TargetRange
Dim img As Object
Call DeleteLastAddedPicture
Application.Wait Now + TimeValue("00:00:01") 'wait 1 sec
If Dir(Path) = "" Then
MsgBox "File not found at: " & Path, vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
Set img = ActiveSheet.Pictures.Insert(Path)
With img
.Left = TargetRange.Left
.Top = TargetRange.Top
.Width = TargetRange.Width
.Height = TargetRange.Height
End With
End Sub
Sub StartupOptions()
Call SendMessage(hWndApp, wm_RunEES, em_DeleteLog, notUsed) 'delete log file
Call DeleteFile(ExampleFolder + "/HeatPumpResults.dat") 'delete output from last run
Call SendMessage(hWndApp, wm_RunEES, em_LogOn, notUsed) 'Start logging
End Sub
Function SetInputs(R As String, T As Range) 'Copy the inputs to EES to text files
Dim RR As String
Dim TInArr As Variant
Call StartupOptions
RR = "'" + R + "'"
TInArr = T.Value
Open ExampleFolder + "\Refrigerant.dat" For Output As #1
Print #1, RR
Close #1
Open ExampleFolder + "\OutdoorTemp.dat" For Output As #2
Print #2, TInArr
Close #2
SetInputs = 1
End Function
Function GetOutputs() As Variant() 'Import the EES outputs and plot
Dim OutArr(1 To 3) As Variant
Dim OutputFile As String
Dim COP, Q_H, m_dot As Variant
OutputFile = ExampleFolder + "\HeatPumpResults.dat"
If (Not OutputFileExists(OutputFile)) Then
MsgBox "Output file " + OutputFile + " was not found"
For i = 1 To 3
OutArr(1) = -999
Next i
Else
Open OutputFile For Input As #3
Input #3, COP, Q_H, m_dot
Close #3
End If
OutArr(1) = COP
OutArr(2) = Q_H
OutArr(3) = m_dot
Call InsertJPG(ExampleFolder + "\PH_plot.jpg", ActiveSheet.Range("A10:H30"))
GetOutputs = OutArr
End Function
Function Solve_EES(R As String, T As Range) As Variant 'Solve the open EES program
Call SetInputs(R, T)
hWndApp = FindWindow("TEES_D", vbNullString)
If (hWndApp = 0) Then
MsgBox "EES is not running. Start EES and open the file that you want to solve."
Solve = GetOutputs()
Exit Function
End If
Result = SendMessage(hWndApp, wm_RunEES, em_Solve, notUsed)
If (Result <> 0) Then
MsgBox "EES returned error #" + Str(Result) + ". See the log file in the EESfolder/EESCallFrom App.log file"
Else
Solve_EES = GetOutputs()
End If
End Function
Function RunMacroTab(R As String, T As Range, TabNo As LongPtr) As Variant
'Solve macro #TabNo in the open EES program.
Call SetInputs(R, T)
hWndApp = FindWindow("TEES_D", vbNullString)
If (hWndApp = 0) Then
MsgBox "EES is not running. Start EES and open the file that contains the Macro window tab that you want to run."
RunMacroTab = GetOutputs()
Exit Function
End If
Result = SendMessage(hWndApp, wm_RunEES, em_RunMacroTab, TabNo)
If (Result <> 0) Then
MsgBox "EES returned error #" + Str(Result) + ". See the log file in the EESfolder/EESCallFrom App.log file"
Else
RunMacroTab = GetOutputs()
End If
End Function
Start EES and open the program shown above. In the EXCEL sheet, create entries for the refrigerant name, outdoor temperature, COP, heating capacity and flowrate as shown.

Select cells D5:F5 and enter =Solve_EES(A5,B5). Press the enter key. {Older EXCEL programs require that you hold the Ctrl-Shift and press enter.} Now, whenever you change the refrigerant name in cell A5 or outdoor temperature in cell B5, EXCEL will call EES and return the COP, capacity, and m_dot in cells D5:F5. A plot will also be returned and displayed, as shown.
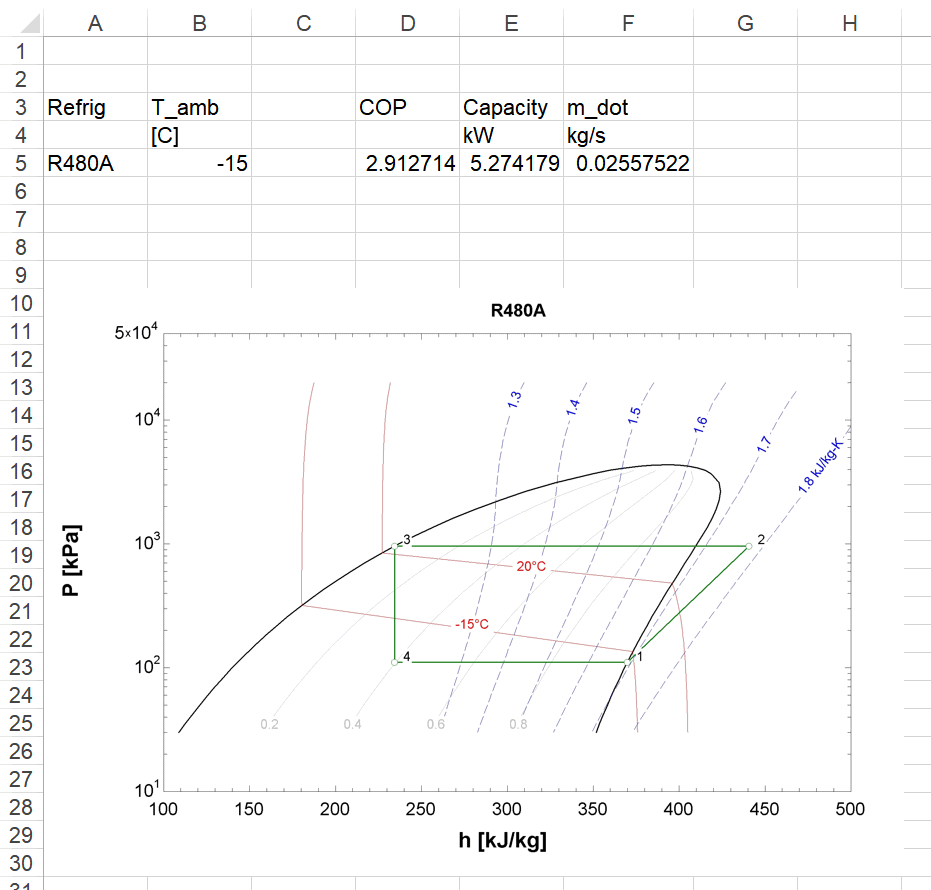
The property plot is imported with Sub InsertJPG. Note that the location of the plot is specified in the call to InsertJPG. It is ActiveSheet.Range("A10:H30") in this example.
Function RunMacroTab will run the macro in a specified tab of the open EES program. It is not needed or used in this example.
Note the only functions SetInputs and GetOutputs and possibly the ExampleFolder need to be modified for other problems.
Any error messages that arise will be written to file EESCallFromApp.log in the EES directory.