Calling EES from LabView
Starting with version 12.131, it is possible to call a Professional version of EES from LabView. The interaction is made using the SendMessage command. It is possible to transfer data to EES using one or more text files that are used to solve a problem and/or run a series of macro commands. EES then writes output files that are read by LabView.
An example illustrating the interaction is provided here. This example calculates the specific volume for a fluid given its temperature and pressure using EES. The property calculation is done in EES but the process is controlled from a LabView VI.
Create a folder where the programs (your LabView vi and the EES program) will both reside. The text files used for communication will also be written in this folder. The python program GetEESHandle.py, listed below, is saved to this folder as well. This python code obtains the EES Window Handle which is needed by the SendMessage command. Note that you may have to install the win32gui library in python if it is not already installed.
import win32gui
import sys
# Callback function for EnumWindows
def enum_windows_callback(hwnd, wildcard):
class_name = win32gui.GetClassName(hwnd)
if class_name == wildcard:
print(hwnd) # prints HWND to stdout
sys.exit(0) # exit once found
# Enumerate all top-level windows
win32gui.EnumWindows(enum_windows_callback, "TEES_D")
The EES program CalculateV.ees, shown below, will read a data file ('C:\LabViewExample\State.dat') that contains a fluid name (R$), temperature (T) and pressure (P). The EES program calculates the specific volume (v) and writes it to a second data file ('C:\LabViewExample\v.dat').
$Import 'C:\MATLABExample\State.dat' R$, T, P
$UnitSystem SI Mass kPa C kJ
v = Volume(R$, T=T, P=P)
$RunMacroAfter
Export 'C:\MATLABExample\v.dat' v
$EndMacro
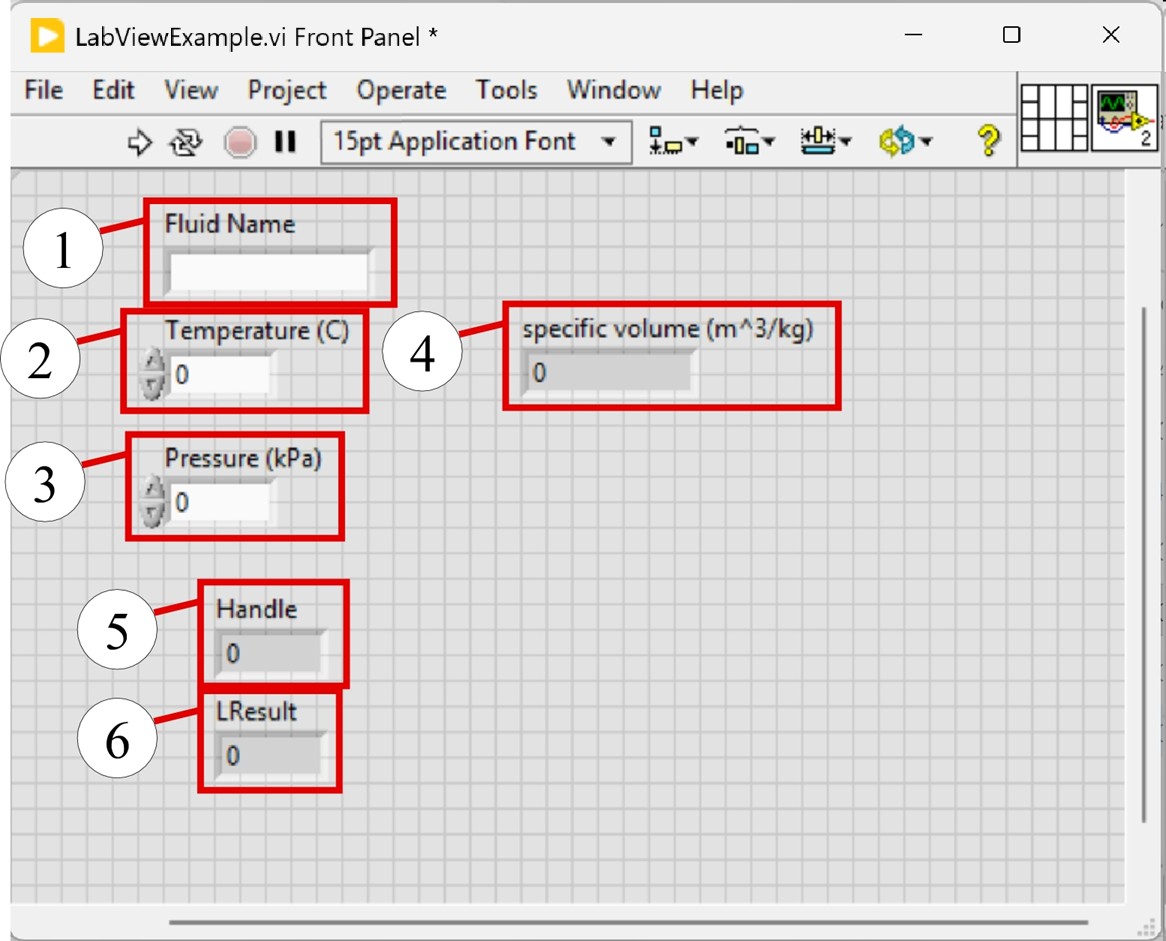
The figure below illustrates the front panel of the LabView vi which has 3 controls (labeled 1, 2, and 3) allowing the user to enter a string for the fluid name (1) and two numbers (2 and 3) corresponding to the temperature and pressure. The front panel also contains 3 indicators (labeled 4, 5, and 6) corresponding to the calculated value of specific volume (4) as well as the Windows Handle for EES (5) and the result returned by the SendMessage command (6). The last two indicators are only for debugging and could be removed.

The figure below illustrates the block diagram for the LabView vi. The controls (1, 2, and 3) and indicators (4, 5, and 6) are evident in the block diagram. The block diagram contains a flat sequence with three panels to control the timing. The first panel creates the string to be written to the file State.dat. This is done by converting the numbers for temperature and pressure to strings using the Number to Fractional String function (7) and then concatenating the string for the fluid (surrounded by single quotes) with the strings for the temperature and pressure, separated by spaces (8). The resulting string is written to the text file using the Write to Text File function (9).
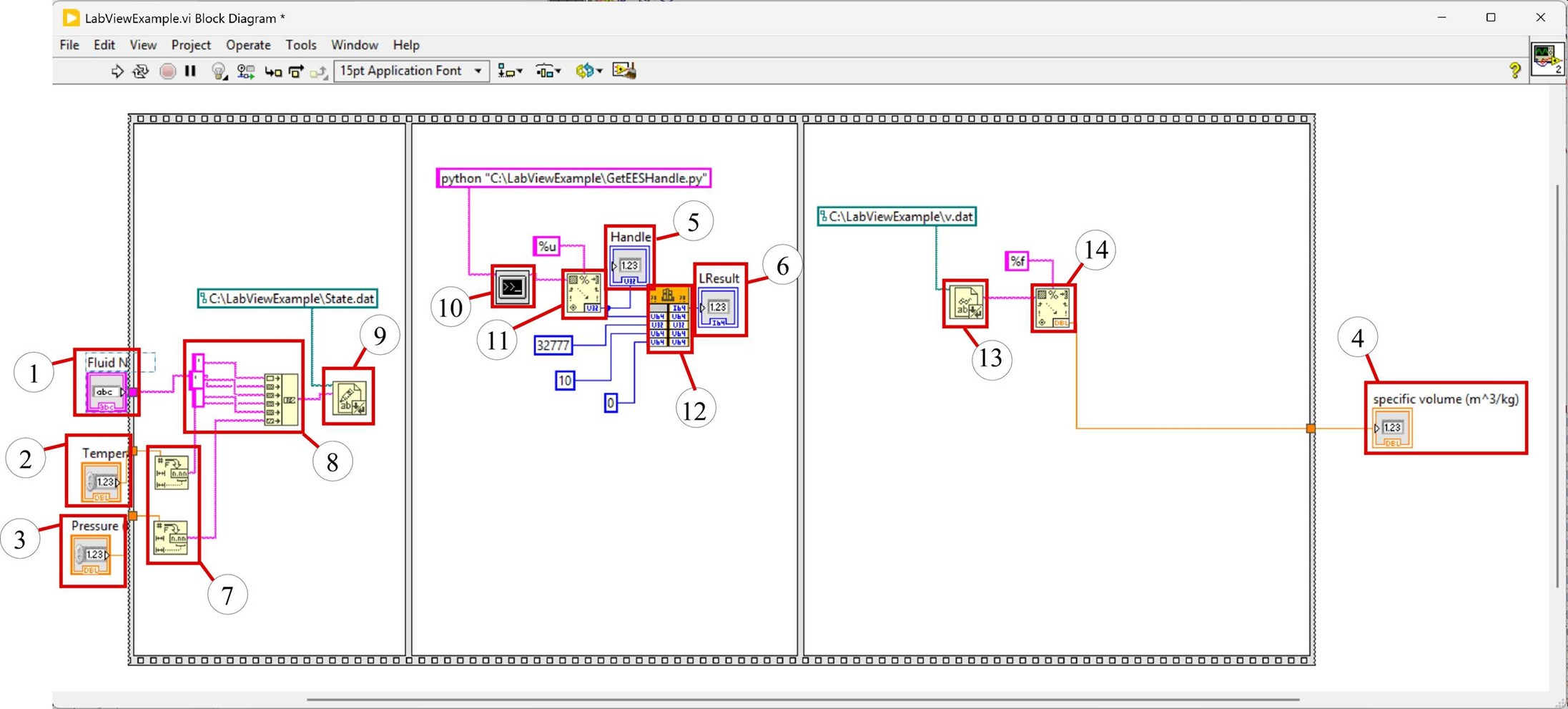
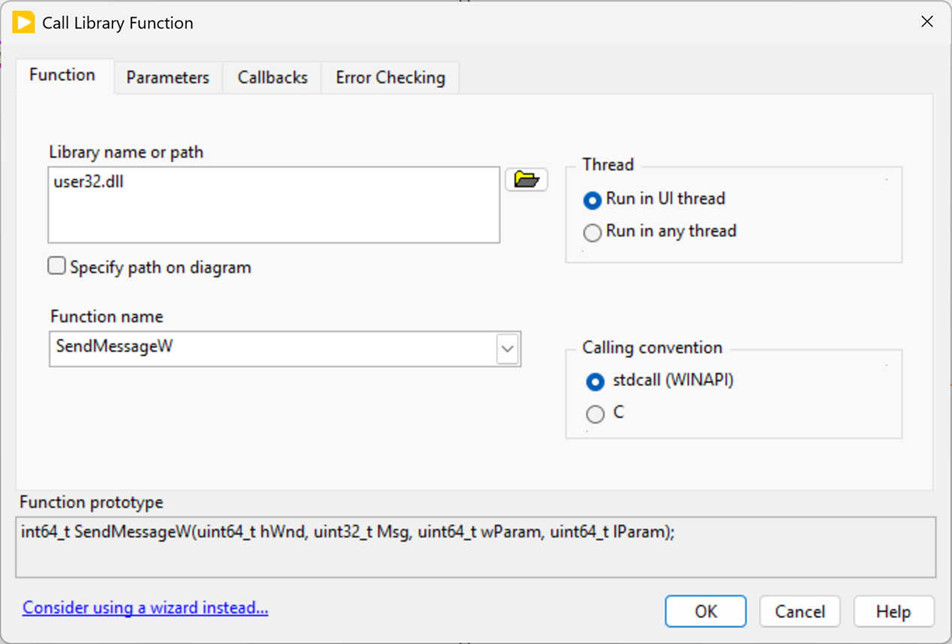
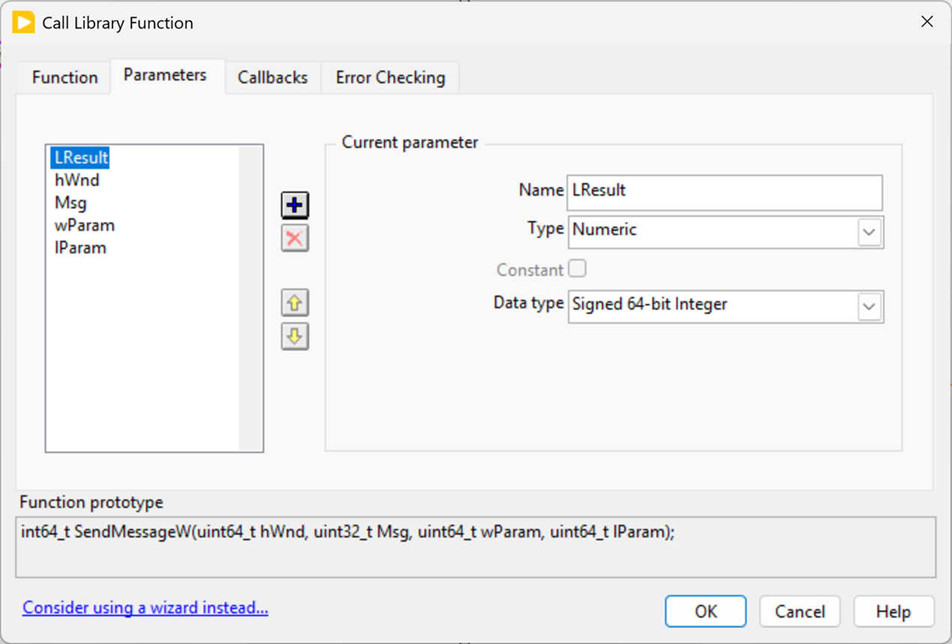
The second panel runs the python code GetEESHandle.py using the System Exec vi (10). The command line to execute is: python "C:\LabViewExample\GetEESHandle.py" and the python code writes the windows handle to the standard output which is then converted to an unsigned integer using the Scan from String vi (11). The Windows Handle is one of several inputs to the SendMessage command that is executed using the Call Library Function Node (12). The Call Library Function node has to be setup carefully, as shown in the screenshots below. The library name is user32.dll and the command to send is SendMessageW using the standards Windows API format. The parameters include the output LResult (a signed 64 bit integer), the Windows handle hWnd (an unsigned 64-bit integer), the identifier message Msg (an unsigned 32-bit integer), the command wParam (an unsigned 64-bit integer), and the extra parameter lParam (an unsigned 64-bit integer).
The third panel reads the file v.dat (13) and converts the text to a numerical answer (14) that is the specific volume.
Any error messages that arise will be written to file EESCallFromApp.log in the EES directory.